IPHY 3410
Instructor: Dr. Leif Saul
Fall 2023

IPHY 3410Instructor: Dr. Leif Saul
|
 |
NOTE: these questions are intended for practice only. They do not reflect all major topics covered in the lectures.
1. Cilia occur in or on:
A. epithelium of upper respiratory tract
B. epithelium of kidney tubules
C. goblet cells
D. A and B
E. A and C
2. The blood is an example of _______ because _________________:
A. connective tissue; it has a large amount of extracellular matrix
B. an organism; it is composed of multiple organ systems
C. muscle tissue; it is capable of movement
D. organ; it is composed of multiple tissues
E. organ system; it is composed of multiple organs
3. Where are you likely to find a circumferential lamella?
A. As the outermost lamella within each osteon
B. Near the periosteum, in spongy bone tissue
C. Near the periosteum, in compact bone tissue
D. A and C
E. All of the above
4. Which of the following is NOT found in the epidermis?
A. Immune cells
B. Desmosomes
C. Mitochondria
D. Sensory cells
E. All of the above are found in the epidermis
5. The alveoli (surface responsible for gas exchange) in the lungs are lined with _____________ epithelium.
A. stratified squamous
B. simple squamous
C. simple columnar
D. pseudostratified columnar
E. transitional
6. Which of the following is/are vascularized?
A. Bone tissue
B. Epidermis
C. Mature cartilage
D. All of the above
E. A and C only
7. Elastic cartilage is found in:
A. Artery walls.
B. Intervertebral discs.
C. Growing bones.
D. Meniscus of knee joint.
E. None of the above.
8. Epithelia give rise to
A. Sebaceous glands
B. Sweat glands
C. Hair follicles
D. All exocrine glands
E. All of the above
9. In compact bone,
A. osteocytes are found embedded within Volkmann's canals.
B. lacunae are connected with each other by canaliculi.
C. blood vessels travel through bone matrix via canals called lacunae.
D. lamellae from different osteons are connected by Haversian canals.
E. Volkmann's canal runs through the central portion of each osteon.
10. The type of membrane that covers the outside (superficial) surface of the major visceral organs is called the:
A. mucous membrane.
B. serous membrane.
C. glandular membrane.
D. squamous membrane.
E. none of the above.
11. Fibroblasts are the characteristic cell type found in which of the following tissues?
A. Fibrocartilage
B. Reticular connective tissue
C. Hyaline cartilage
D. Bone
E. All of the above
12. Endochondral formation of a long bone
A. Continues in the epiphyseal plates throughout your life
B. Involves bone cells dying and being replaced by cartilage cells
C. Is completed prior to birth
D. Involves producing new bone tissue at the articular cartilages
E. Involves secreting bone matrix on calcified cartilage
13. Which of the following is/are effective at resisting tension (pulling) forces:
A. Intermediate filaments
B. Collagen
C. Keratin
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
14. Which epidermal layer is absent in thin skin?
A. stratum spinosum
B. stratum granulosum
C. stratum corneum
D. stratum lucidum
E. stratum basale
15. The dermis
A. contains blood vessels
B. contains glands that secrete oil
C. contains elastic fibers
D. A and C
E. All of the above
16. Hyaline cartilage can be found in the:
A. articular surface of an epiphysis.
B. epiphyseal line.
C. epiglottis.
D. external ear.
E. A and B.
17. Adipose tissue is an important feature of:
A. epidermis
B. dermis
C. hypodermis
D. basement membrane
E. stratum corneum
18. Suppose you are constructing a new epithelium. You take a layer of squamous cells, and on its apical surface you place a layer of columnar cells. According to the rules for naming epithelia, this would be a:
A. Stratified columnar epithelium
B. Stratified squamous epithelium
C. Transitional epithelium
D. Simple columnar epithelium
E. Simple squamous epithelium
19. Most of the bones of the skeleton are formed by:
A. intramembranous bone formation.
B. cartilaginous bone formation.
C. periosteal bone formation.
D. endochondral bone formation.
E. appositional bone formation.
20. A thermometer breaks, and you unwisely handle the exposed liquid mercury, which passes through your skin and reaches your blood. Which of the following MUST the mercury pass through on its way to the blood?
A. Hypodermis
B. Stratum lucidum
C. Endothelium
D. B and C
E. All of the above
21. Which of the following tissue types has the greatest capacity for regeneration and proliferation?
A. Epithelium.
B. Connective tissue.
C. Nervous tissue.
D. Muscle tissue.
E. Collagen tissue.
22. Which of the following is (are) found in spongy bone?
A. Osteoid.
B. Osteon.
C. Central canal.
D. All of the above.
E. A and B.
23. Collagen is a significant component of:
A. The ground substance in bone
B. The fibrous component of bone
C. Stratified squamous epithelium
D. A and B
E. None of the above
Questions 24 and 25 refer to the diagram below which shows a simplified cross section through the abdomen, like the "body cavities and membranes" diagrams presented in lecture, but ignoring the outer layers. "Space" indicates the space where food sits inside the stomach. The layers "1" and "2" are separated by a basement membrane and together comprise a multicellular membrane.
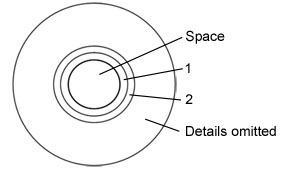
24. Assuming the stomach lining is typical of the digestive tract, what is layer 1?
A. Mucous membrane
B. Simple columnar epithelium
C. Stratified squamous epithelium
D. Areolar connective tissue
E. Mesothelium
25. Layer 2 is
A. Lamina propria
B. Muscle
C. Endothelium
D. Avascular
E. None of the above
26. Which is true of all three types of cartilage?
A. Ground substance attracts & holds a large amount of water
B. Has lacunae
C. Has elastic fibers
D. A and B
E. All of the above
27. What do areolar connective tissue, reticular connective tissue, and adipose tissue have in common?
A. They are all specialized for defense against pathogens
B. They are all highly resilient when subjected to compressive forces
C. They are all loose connective tissues
D. They are all found in the skin
E. They are all non-vascularized tissues
28. 206 is the number of
A. Bones in an infant
B. Closed body cavities
C. Tissue types in the body
D. Cell layers in thick skin
E. None of the above
29. You are shrunk down to microscopic size, magically transported into the body of your roommate, and find that your feet are standing on the apical surface of a mesothelium, and the rest of your body is surrounded by fluid. The fluid is:
A. The interstitial fluid of an areolar connective tissue.
B. The mucus lining on the mucosa of a hollow organ.
C. Serous fluid, which is produced mainly by secretion.
D. Serous fluid, which is produced mainly by filtration.
E. Blood plasma.
30. Tactile epithelial cells are found in the:
A. Stratum spinosum
B. Stratum corneum
C. Stratum lucidum
D. Stratum granulosum
E. Stratum basale
31. Osteoclasts
A. Are more active than osteoblasts in the condition known as osteomalacia
B. Are more active than osteoblasts in the condition known as achondroplasia
C. Are confined within lacunae
D. Are larger than other bone cells
E. None of the above
32. In the idealized diagram of body cavities and membranes that was presented in class, which of the following lists layers and/or spaces in correct order, from superficial to deep?
A. Visceral serosa, parietal serosa, mucosa
B. Cutaneous membrane, mucous membrane, visceral serosa
C. Parietal serosa, lumen, visceral serosa
D. Mucous membrane, parietal serosa, cutaneous membrane
E. Serous cavity, visceral serosa, mucosa
33. In endochondral bone formation, place the following events in the correct order, from early to late:
(1) Bone collar appears (2) Cavity appears in diaphysis (3) Periosteum appears (4) Periosteal bud invades diaphysis
A. 3,1,2,4
B. 2,4,3,1
C. 4,2,1,3
D. 3,4,2,1
E. 1,2,4,3
34. What do mesothelium and endothelium have in common?
A. They both are simple squamous epithelium.
B. They both are stratified squamous epithelium.
C. They both are part of the same continuous sheet of epithelium that is folded into inner and outer parts.
D. They both are connective tissues.
E. They both enclose spaces that are continuous with the outside world.
35. Mesenchyme gives rise to all
A. Adipose tissue
B. Exocrine glands
C. Endocrine glands
D. Epithelia
E. All of the above
36. Which of the following features is a component of compact bone tissue?
A. Gap junctions
B. Chondrocytes
C. Trabeculae
D. Periosteum
E. Yellow marrow
37. Which of the following is NOT a component of the ground substance in ANY connective tissue?
A. Hydroxyapatite
B. Interstitial fluid
C. Calcium phosphate
D. Elastic fibers
E. All of the above are found as a component of ground substance in at least some connective tissue
38. Blood vessels are a component of
A. Bone tissue
B. Bones (i.e. the organs known as bones)
C. Cartilage tissue
D. A and B
E. All of the above
39. At the very center of a mature osteon, what are you most likely to find?
A. Solid bone matrix
B. Osteocytes
C. Spongy bone tissue
D. Blood vessels
E. Any of the above are equally likely
40. Which feature is true of ALL connective tissues?
A. Not innervated.
B. Mostly made of collagen.
C. Vascularized.
D. Connected to a basement membrane.
E. None of the above.
41. In longitudinal bone growth in a long bone, place the following steps in correct relative position from the epiphyseal side to the diaphyseal side:
(1) Chondrocytes die (2) Cartilage matrix calcifies (3) Osteoblasts deposit bone matrix (4) Cartilage grows (5) Osteoclasts remove bone matrix
A. 4,2,1,3,5
B. 5,4,1,3,2
C. 5,1,2,4,3
D. 4,2,5,3,1
E. 1,4,2,3,5
Questions 42 and 43 refer to the diagram below that was presented and labeled in class.
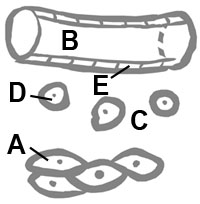
42. The cell labeled A receives its oxygen and nutrients directly from
A. Blood, indicated by B
B. Blood, indicated by C
C. Interstitial fluid, indicated by B
D. Interstitial fluid, indicated by C
E. The cell indicated by D
43. Cell D is most likely a ___ and is a part of ___ tissue.
A. Blood cell; areolar connective tissue
B. Fibroblast; areolar connective tissue
C. Fat cell; adipose tissue
D. Immune cell; reticular connective tissue
E. Muscle cell; smooth muscle tissue
ANSWERS
1 A
2 A
3 C
4 E
5 B
6 A
7 E
8 E
9 B
10 B
11 B
12 E
13 D
14 D
15 E
16 A
17 C
18 A
19 D
20 C
21 A
22 A
23 B
24 B
25 A
26 D
27 C
28 E
29 D
30 E
31 D
32 E
33 A
34 A
35 A
36 A
37 D
38 B
39 D
40 E
41 A
42 D
43 B