


 |
(MIDI player required) |
Republic of Chad
In December 1990, after Chad had endured decades of civil warfare among ethnic groups as well as invasions by Libya, former northern guerrilla leader Idriss DEBY seized control of the government. His transitional government eventually suppressed or came to terms with most political-military groups, settled the territorial dispute with Libya on terms favorable to Chad, drafted a democratic constitution which was ratified by popular referendum in March 1996, held multiparty national presidential elections in June and July 1996 (DEBY won with 67% of the vote), and held multiparty elections for the National Assembly in January and February 1997, in which Idriss DEBY's party, Patriotic Salvation Movement or MPS, won a majority of the seats.
Location: Central Africa, south of Libya
Geographic coordinates: 15 00 N, 19 00 E
Map references: Africa
Area:
total: 1.284 million sq km
land: 1,259,200 sq km
water: 24,800 sq km
Area—comparative: slightly more than three times the size of California
Land boundaries:
total: 5,968 km
border countries: Cameroon 1,094 km, Central African Republic
1,197 km, Libya 1,055 km, Niger 1,175 km, Nigeria 87 km, Sudan 1,360 km
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims: none (landlocked)
Climate: tropical in south, desert in north
Terrain: broad, arid plains in center, desert in north, mountains in northwest, lowlands in south
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Djourab Depression 175 m
highest point: Emi Koussi 3,415 m
Natural resources: petroleum (unexploited but exploration under way), uranium, natron, kaolin, fish (Lake Chad)
Land use:
arable land: 3%
permanent crops: 0%
permanent pastures: 36%
forests and woodland: 26%
other: 35% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 140 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: hot, dry, dusty harmattan winds occur in north; periodic droughts; locust plagues
Environment—current issues: inadequate supplies of potable water; improper waste disposal in rural areas contributes to soil and water pollution; desertification
Environment—international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered
Species, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping
Geography—note: landlocked; Lake Chad is the most significant water body in the Sahel
Population: 7,359,512 (July 1998 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 44% (male 1,631,010; female 1,623,272)
15-64 years: 53% (male 1,903,012; female 1,982,257)
65 years and over: 3% (male 97,118; female 122,843) (July 1998
est.)
Population growth rate: 2.66% (1998 est.)
Birth rate: 43.45 births/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Death rate: 16.86 deaths/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/female (1998 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 116.97 deaths/1,000 live births (1998 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 48.22 years
male: 45.81 years
female: 50.73 years (1998 est.)
Total fertility rate: 5.74 children born/woman (1998 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Chadian(s)
adjective: Chadian
Ethnic groups: Muslims (Arabs, Toubou, Hadjerai, Fulbe, Kotoko, Kanembou, Baguirmi, Boulala, Zaghawa, and Maba), non-Muslims (Sara, Ngambaye, Mbaye, Goulaye, Moundang, Moussei, Massa), nonindigenous 150,000 (of whom 1,000 are French)
Religions: Muslim 50%, Christian 25%, indigenous beliefs (mostly animism) 25%
Languages: French (official), Arabic (official), Sara and Sango (in south), more than 100 different languages and dialects
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write in French or
Arabic
total population: 48.1%
male: 62.1%
female: 34.7% (1995 est.)
Country name:
conventional long form: Republic of Chad
conventional short form: Chad
local long form: Republique du Tchad
local short form: Tchad
Data code: CD
Government type: republic
National capital: N'Djamena
Administrative divisions: 14 prefectures (prefectures, singular—prefecture); Batha, Biltine, Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti, Chari-Baguirmi, Guera, Kanem, Lac, Logone Occidental, Logone Oriental, Mayo-Kebbi, Moyen-Chari, Ouaddai, Salamat, Tandjile
Independence: 11 August 1960 (from France)
National holiday: Independence Day, 11 August (1960)
Constitution: 31 March 1995, passed by referendum
Legal system: based on French civil law system and Chadian customary law; does not accept compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: President Lt. Gen. Idriss DEBY (since 4 December 1990)
head of government: Prime Minister Nassour Guelengdouksia OUAIDOU (since
16 May 1997); appointed by the president; note—he was reappointed on 1
January 1998 when President DEBY named his new government
cabinet: Council of State appointed by the president on the recommendation
of the prime minister
elections: the constitution provides for the election of a president
by direct popular vote to serve a term of five years; if no candidate receives
at least 50% of the total vote, the two candidates receiving the most votes
must stand for a second round of voting; last held 2 June and 11 July 1996
(next to be held NA 2001); the prime minister is appointed by the president
election results: in the first round of voting none of the 15 candidates
received the required 50% of the total vote; percent of vote, first round—Lt.
Gen. Idress DEBY 47.8%; percent of vote, second round—Lt. Gen. DEBY 69.1%,
Wadal Abdelkader KAMOUGUE 30.9%
Legislative branch: unicameral National Assembly (125 seats; members
serve four-year terms); replaces the Higher Transitional Council or the
Conseil Superieur de Transition
elections: National Assembly—last held in two rounds on 5 January and
23 February 1997, (next to be held NA 2001); in the first round of voting
on 5 January 1997 some candidates won clear victories by receiving 50%
or more of the vote; where that did not happen, the two highest scoring
candidates stood for a second round of voting
election results: percent of vote by party—NA; seats by party—MPS 65,
URD 29, UNDR 15, RDP 3, others 13
Judicial branch: Supreme Court; Court of Appeal; Criminal Courts; Magistrate Courts
Political parties and leaders: Patriotic Salvation Movement or MPS [Maldom Bada ABBAS, chairman], originally in opposition but now the party in power and the party of the president; National Union for Development and Renewal or UNDR [Saleh KEBZABO, leader]; Rally for Democracy and Progress or RDP [Lal Mahamat CHOUA, leader]; Union for Renewal and Democracy or URD [Gen. Wadal Abdelkader KAMOUGUE, leader]; note—in mid-1996 Chad had about 60 political parties, of which these are the most prominent in the new National Assembly
International organization participation: ACCT, ACP, AfDB, BDEAC, CEEAC, ECA, FAO, FZ, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, ITU, NAM, OAU, OIC, UDEAC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCL, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Mahamat Saleh AHMAT
chancery: 2002 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone: [1] (202) 462-4009
FAX: [1] (202) 265-1937
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador David C. HALSTED
embassy: Avenue Felix Eboue, N'Djamena
mailing address: B. P. 413, N'Djamena
telephone: [235] (51) 70-09, (51) 90-52, (51) 92-33
FAX: [235] (51) 56-54
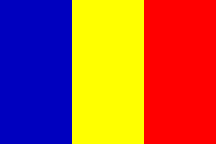
Flag description: three equal vertical bands of blue (hoist side), yellow, and red; similar to the flag of Romania; also similar to the flag of Andorra, which has a national coat of arms featuring a quartered shield centered in the yellow band; design was based on the flag of France
Economy—overview: Landlocked Chad's economic development suffers from it's geographic remoteness, drought, lack of infrastructure, and political turmoil. About 85% of the population depends on agriculture, including the herding of livestock. Of Africa's Francophone countries, Chad benefited least from the 50% devaluation of their currencies in January 1994. Financial aid from the World Bank, the African Development Fund, and other sources is directed largely at the improvement of agriculture, especially livestock production. Lack of financing, however, is stalling the development of a southern oil field and the construction of a proposed oil pipeline through Cameroon.
GDP: purchasing power parity—$4.3 billion (1997 est.)
GDP—real growth rate: 5.5% (1997 est.)
GDP—per capita: purchasing power parity—$600 (1997 est.)
GDP—composition by sector:
agriculture: 48%
industry: 18%
services: 34% (1995)
Inflation rate—consumer price index: 15% (1997 est.)
Labor force: NA
by occupation: agriculture 85% (subsistence farming, herding, and fishing)
Unemployment rate: NA%
Budget:
revenues: $198 million
expenditures: $218 million, including capital expenditures of $146
million (1998 est.)
Industries: cotton textiles, meat packing, beer brewing, natron (sodium carbonate), soap, cigarettes, construction materials
Industrial production growth rate: 5% (1995)
Electricity—capacity: 29,000 kW (1995)
Electricity—production: 80 million kWh (1995)
Electricity—consumption per capita: 14 kWh (1995)
Agriculture—products: cotton, sorghum, millet, peanuts, rice, potatoes, manioc (tapioca); cattle, sheep, goats, camels
Exports:
total value: $259 million (f.o.b., 1996 est.)
commodities: cotton, cattle, textiles
partners: Portugal 30%, Germany 18%, South Africa 16%, France 7%
Imports:
total value: $301 million (f.o.b., 1996 est.)
commodities: machinery and transportation equipment 39%, industrial
goods 20%, petroleum products 13%, foodstuffs 9%; textiles; note—excludes
military equipment
partners: France 34%, Cameroon 24%, Nigeria 7%, US 6%
Debt—external: $875 million (1995 est.)
Economic aid:
recipient: $125 million committed by Taiwan (August 1997); $30 million
committed by African Development Bank
Currency: 1 Communaute Financiere Africaine franc (CFAF) = 100 centimes
Exchange rates: CFA Francs (CFAF) per US$1—608.36 (January 1998), 583.67
(1997), 511.55 (1996), 499.15 (1995), 555.20 (1994), 283.16 (1993)
note: beginning 12 January 1994 the CFA franc was devalued to CFAF
100 per French franc from CFAF 50 at which it had been fixed since 1948
Fiscal year: calendar year
Telephones: 5,000 (1987 est.)
Telephone system: primitive system
domestic: fair system of radiotelephone communication stations
international: satellite earth station—1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean)
Radio broadcast stations: AM 6, FM 1, shortwave 0
Radios: NA
Television broadcast stations: 1 (1987 est.)
note: limited TV service; many facilities are inoperative
Televisions: 7,000 (1991 est.)
Railways: 0 km
Highways:
total: 32,700 km
paved: 262 km
unpaved: 32,438 km (1995 est.)
Waterways: 2,000 km navigable
Ports and harbors: none
Airports: 53 (1997 est.)
Airports—with paved runways:
total: 6
over 3,047 m: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
under 914 m: 1 (1997 est.)
Airports—with unpaved runways:
total: 47
1,524 to 2,437 m: 16
914 to 1,523 m: 21
under 914 m: 10 (1997 est.)
Military branches: Armed Forces (includes Ground Force, Air Force, and Gendarmerie), Republican Guard, Police
Military manpower—military age: 20 years of age
Military manpower—availability:
males age 15-49: 1,645,295 (1998 est.)
Military manpower—fit for military service:
males: 852,705 (1998 est.)
Military manpower—reaching military age annually:
males: 68,343 (1998 est.)
Military expenditures—dollar figure: $74 million (1994)
Military expenditures—percent of GDP: 11.1% (1994)
Disputes—international: demarcation of international boundaries in the vicinity of Lake Chad, the lack of which led to border incidents in the past, is completed and awaits ratification by Cameroon, Chad, Niger, and Nigeria
This page last updated on 27 June 1999
Designed by Britt A. Cartrite,
1999