


 |
(MIDI player required) |
| Geography |
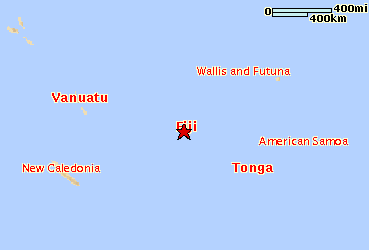
Location: Oceania, island group in the South Pacific Ocean, about two-thirds of the way from Hawaii to New Zealand
Geographic coordinates: 18 00 S, 175 00 E
Map references: Oceania
Area:
total: 18,270 sq km
land: 18,270 sq km
water: 0 sq km
Area—comparative: slightly smaller than New Jersey
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 1,129 km
Maritime claims: measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation; rectilinear shelf claim
added
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate: tropical marine; only slight seasonal temperature variation
Terrain: mostly mountains of volcanic origin
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: Tomanivi 1,324 m
Natural resources: timber, fish, gold, copper, offshore oil potential
Land use:
arable land: 10%
permanent crops: 4%
permanent pastures: 10%
forests and woodland: 65%
other: 11% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 10 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: cyclonic storms can occur from November to January
Environment—current issues: deforestation; soil erosion
Environment—international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Marine
Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber
83, Tropical Timber 94, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography—note: includes 332 islands of which approximately 110 are inhabited
| People |
Population: 802,611 (July 1998 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 34% (male 139,713; female 134,220)
15-64 years: 63% (male 251,646; female 251,425)
65 years and over: 3% (male 12,051; female 13,556) (July 1998 est.)
Population growth rate: 1.28% (1998 est.)
Birth rate: 22.92 births/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Death rate: 6.25 deaths/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Net migration rate: -3.92 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.89 male(s)/female (1998 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 16.65 deaths/1,000 live births (1998 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 66.29 years
male: 63.92 years
female: 68.78 years (1998 est.)
Total fertility rate: 2.74 children born/woman (1998 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Fijian(s)
adjective: Fijian
Ethnic groups: Fijian 49%, Indian 46%, European, other Pacific Islanders, overseas Chinese, and other 5%
Religions: Christian 52% (Methodist 37%, Roman Catholic 9%), Hindu 38%, Muslim
8%, other 2%
note: Fijians are mainly Christian, Indians are Hindu, and there is a Muslim
minority (1986)
Languages: English (official), Fijian, Hindustani
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 91.6%
male: 93.8%
female: 89.3% (1995 est.)
| Government |
Country name:
conventional long form: Republic of the Fiji Islands
conventional short form: Fiji
Data code: FJ
Government type: republic
note: military coup leader Maj. Gen. Sitiveni RABUKA formally declared Fiji
a republic on 6 October 1987
National capital: Suva
Administrative divisions: 4 divisions and 1 dependency*; Central, Eastern, Northern, Rotuma*, Western
Independence: 10 October 1970 (from UK)
National holiday: Independence Day, 10 October (1970)
Constitution: 10 October 1970 (suspended 1 October 1987); a new constitution was proposed on 23 September 1988 and promulgated on 25 July 1990; another new constitution, which opens the way for a non-ethnic Fijian to become prime minister, was signed by the president on 25 July 1997 and will come into force no later than 28 July 1998
Legal system: based on British system
Suffrage: 21 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: President Ratu Sir Kamisese MARA (acting president since 15 December
1993, president since 12 January 1994); First Vice President Ratu Sir Josaia
TAIVAI'IA (since 12 January 1994); Second Vice President Ratu Inoke TAKIVEIKATA
(since 12 January 1994)
head of government: Prime Minister Sitiveni RABUKA (since 2 June 1992); Deputy Prime Minister
Taufa VAKATALE (since 7 August 1997)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the prime minister from among the members of Parliament
and is responsible to Parliament
note: there is also a Presidential Council that advises the president on matters
of national importance and a Great Council of Chiefs which consists of the
highest ranking members of the traditional chiefly system
elections: president elected by the Great Council of Chiefs for a five-year term;
prime minister appointed by the president
election results: Ratu Sir Kamisese MARA elected president; percent of Great Council of
Chiefs vote—NA
Legislative branch: bicameral Parliament consists of the Senate (34 seats; 24 reserved for
ethnic Fijians, 9 for Indians and others, and 1 for the island of Rotuma;
members appointed by the president to serve five-year terms) and the House
of Representatives (70 seats; 37 reserved for ethnic Fijians, 27 for ethnic
Indians, and 6 for independents and others; members elected by popular vote
on a communal basis to serve five-year terms)
elections: House of Representatives—last held 18-25 February 1994 (next to be
held NA 1999)
election results: House of Representatives—percent of vote by party—NA; seats by party
- SVT 31, NFP 20, FLP 7, FAP 5, GVP 4, independents 2, ANC 1
note: when the new constitution comes into force, the composition of the legislative
branch will change to the following: Senate—32 seats (14 appointed by the
Great Council of Chiefs, nine appointed by the prime minister, eight appointed
by the leader of the opposition, and one appointed by the Council of Rotuma);
House of Representatives—71 seats (23 reserved for ethnic Fijians, 19 reserved
for ethnic Indians, three reserved for other ethnic groups, and there will
be 25 open seats)
Judicial branch: Supreme Court, judges are appointed by the president
Political parties and leaders: Fijian Political Party (SVT—primarily Fijian), leader Maj. Gen. Sitivini
RABUKA; National Federation Party (NFP; primarily Indian), Jai Ram REDDY;
Fijian Nationalist Party (FNP), Sakeasi BUTADROKA; Fiji Labor Party (FLP),
Mahendra CHAUDHRY; General Voters Party (GVP), Leo SMITH; Fiji Conservative
Party (FCP), leader NA; Conservative Party of Fiji (CPF), leader NA; Fiji
Indian Liberal Party, leader NA; Fiji Indian Congress Party, leader NA; Fiji
Independent Labor (Muslim), leader NA; Four Corners Party, leader NA; Fijian
Association Party (FAP), Ratu Finau MARA; General Electors' Association, David
PICKERING
note: in early 1995, ethnic Fijian members of the All National Congress (ANC)
merged with the Fijian Association (FA); the remaining members of the ANC
have renamed their party the General Electors' Association
International organization participation: ACP, AsDB, C, CP, ESCAP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, ISO (subscriber), ITU, PCA, Sparteca, SPC, SPF, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNIKOM, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTrO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Ratu Napolioni MASIREWA
chancery: Suite 240, 2233 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: [1] (202) 337-8320
FAX: [1] (202) 337-1996
consulate(s): New York
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Larry M. DINGER
embassy: 31 Loftus Street, Suva
mailing address: P. O. Box 218, Suva
telephone: [679] 314466
FAX: [679] 300081
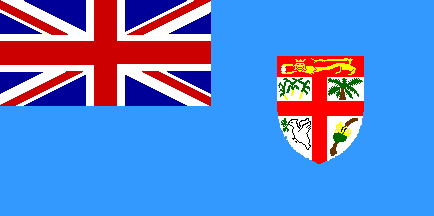
Flag description: light blue with the flag of the UK in the upper hoist-side quadrant and the Fijian shield centered on the outer half of the flag; the shield depicts a yellow lion above a white field quartered by the cross of Saint George featuring stalks of sugarcane, a palm tree, bananas, and a white dove
| Economy |
Economy—overview: Fiji, endowed with forest, mineral, and fish resources, is one of the most developed of the Pacific island economies, though still with a large subsistence sector. Sugar exports and a growing tourist industry are the major sources of foreign exchange. Sugar processing makes up one-third of industrial activity. Roughly 250,000 tourists visit each year. Political uncertainty and drought, however, contribute to substantial fluctuations in earnings from tourism and sugar and to the emigration of skilled workers. Fiji's growth slowed in 1997 because the sugar industry suffered from low world prices and rent disputes between farmers and landowners.
GDP: purchasing power parity—$5.1 billion (1996 est.)
GDP—real growth rate: 3% (1996)
GDP—per capita: purchasing power parity—$6,500 (1996 est.)
GDP—composition by sector:
agriculture: 21%
industry: 18%
services: 61% (1995 est.)
Inflation rate—consumer price index: 3% (1997 est.)
Labor force:
total: 235,000
by occupation: subsistence agriculture 67%, wage earners 18%, salary earners 15% (1987)
Unemployment rate: 6% (1997 est.)
Budget:
revenues: $540.65 million
expenditures: $742.65 million, including capital expenditures of $NA (1997 est.)
Industries: sugar, tourism, copra, gold, silver, clothing, lumber, small cottage industries
Industrial production growth rate: 2.9% (1995)
Electricity—capacity: 200,000 kW (1995)
Electricity—production: 545 million kWh (1995)
Electricity—consumption per capita: 705 kWh (1995)
Agriculture—products: sugarcane, coconuts, cassava (tapioca), rice, sweet potatoes, bananas; cattle, pigs, horses, goats; fish catch 13,796 tons (1991)
Exports:
total value: $639 million (f.o.b., 1996)
commodities: sugar 32%, clothing, gold, processed fish, lumber
partners: EU 26%, Australia 15%, other Pacific island countries 11%, Japan 6%
Imports:
total value: $947 million (c.i.f., 1996)
commodities: machinery and transport equipment, petroleum products, food, consumer
goods, chemicals
partners: Australia 30%, NZ 17%, Japan 13%, EU 6%, US 6%
Debt—external: $333.8 million (1996 est.)
Economic aid:
recipient: ODA, $14.35 million from Australia (FY96/97 est.); $3.5 million from
New Zealand (FY95/96)
Currency: 1 Fijian dollar (F$) = 100 cents
Exchange rates: Fijian dollars (F$) per US$1—1.9064 (January 1998), 1.4437 (1997), 1.4033 (1996), 1.4063 (1995), 1.4641 (1994), 1.5418 (1993)
Fiscal year: calendar year
| Communications |
Telephones: 60,017 (1987 est.)
Telephone system: modern local, interisland, and international (wire/radio integrated)
public and special-purpose telephone, telegraph, and teleprinter facilities;
regional radio communications center
domestic: NA
international: access to important cable link between US and Canada and NZ and Australia;
satellite earth station—1 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean)
Radio broadcast stations: AM 7, FM 1, shortwave 0
Radios: NA
Television broadcast stations: 0
Televisions: 12,000 (1992 est.)
| Transportation |
Railways:
total: 597 km; note—belongs to the government-owned Fiji Sugar Corporation
narrow gauge: 597 km 0.610-m gauge (1995)
Highways:
total: 3,440 km
paved: 1,692 km
unpaved: 1,748 km (1996 est.)
Waterways: 203 km; 122 km navigable by motorized craft and 200-metric-ton barges
Ports and harbors: Labasa, Lautoka, Levuka, Savusavu, Suva
Merchant marine:
total: 6 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 17,800 GRT/18,034 DWT
ships by type: chemical tanker 2, oil tanker 1, passenger 1, roll-on/roll-off cargo
2 (1997 est.)
Airports: 24 (1997 est.)
Airports—with paved runways:
total: 3
over 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (1997 est.)
Airports—with unpaved runways:
total: 21
914 to 1,523 m: 4
under 914 m: 17 (1997 est.)
| Military |
Military branches: Republic of Fiji Military Forces (RFMF; includes army, navy, and a small air wing)
Military manpower—military age: 18 years of age
Military manpower—availability:
males age 15-49: 214,475 (1998 est.)
Military manpower—fit for military service:
males: 118,181 (1998 est.)
Military manpower—reaching military age annually:
males: 9,180 (1998 est.)
Military expenditures—dollar figure: $32 million (1997)
Military expenditures—percent of GDP: 5% (1997)
| Transnational Issues |
Disputes—international: none
This page last updated on 19 August 1999.
Designed by Britt A. Cartrite,
1999