


 |
(MIDI player required) |
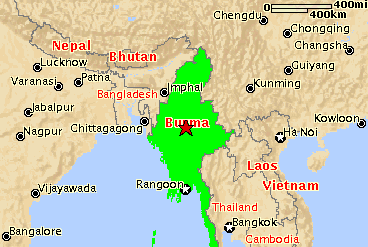
Myanmar (Burma)
Location: Southeastern Asia, bordering the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal, between Bangladesh and Thailand
Geographic coordinates: 22 00 N, 98 00 E
Map references: Southeast Asia
Area:
total: 678,500 sq km
land: 657,740 sq km
water: 20,760 sq km
Area—comparative: slightly smaller than Texas
Land boundaries:
total: 5,876 km
border countries: Bangladesh 193 km, China 2,185 km, India 1,463 km,
Laos 235 km, Thailand 1,800 km
Coastline: 1,930 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone: 24 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate: tropical monsoon; cloudy, rainy, hot, humid summers (southwest monsoon, June to September); less cloudy, scant rainfall, mild temperatures, lower humidity during winter (northeast monsoon, December to April)
Terrain: central lowlands ringed by steep, rugged highlands
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Andaman Sea 0 m
highest point: Hkakabo Razi 5,881 m
Natural resources: petroleum, timber, tin, antimony, zinc, copper, tungsten, lead, coal, some marble, limestone, precious stones, natural gas
Land use:
arable land: 15%
permanent crops: 1%
permanent pastures: 1%
forests and woodland: 49%
other: 34% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 10,680 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: destructive earthquakes and cyclones; flooding and landslides common during rainy season (June to September); periodic droughts
Environment—current issues: deforestation; industrial pollution of air, soil, and water; inadequate sanitation and water treatment contribute to disease
Environment—international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Law of the
Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical
Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography—note: strategic location near major Indian Ocean shipping lanes
Population: 47,305,319 (July 1998 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 36% (male 8,798,474; female 8,461,791)
15-64 years: 59% (male 14,052,386; female 14,019,244)
65 years and over: 5% (male 888,773; female 1,084,651) (July 1998 est.)
Population growth rate: 1.65% (1998 est.)
Birth rate: 28.96 births/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Death rate: 12.51 deaths/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.82 male(s)/female (1998 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 78.35 deaths/1,000 live births (1998 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 54.51 years
male: 53.03 years
female: 56.08 years (1998 est.)
Total fertility rate: 3.7 children born/woman (1998 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Burmese (singular and plural)
adjective: Burmese
Ethnic groups: Burman 68%, Shan 9%, Karen 7%, Rakhine 4%, Chinese 3%, Mon 2%, Indian 2%, other 5%
Religions: Buddhist 89%, Christian 4% (Baptist 3%, Roman Catholic 1%), Muslim 4%, animist beliefs 1%, other 2%
Languages: Burmese, minority ethnic groups have their own languages
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 83.1%
male: 88.7%
female: 77.7% (1995 est.)
Country name:
conventional long form: Union of Burma
conventional short form: Burma
local long form: Pyidaungzu Myanma Naingngandaw (translated by the
US Government as Union of Myanma and by the Burmese as Union of Myanmar)
local short form: Myanma Naingngandaw
former: Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma
Data code: BM
Government type: military regime
National capital: Rangoon (regime refers to the capital as Yangon)
Administrative divisions: 7 divisions* (yin-mya, singular—yin) and 7 states (pyine-mya, singular - pyine); Chin State, Ayeyarwady*, Bago*, Kachin State, Kayin State, Kayah State, Magway*, Mandalay*, Mon State, Rakhine State, Sagaing*, Shan State, Tanintharyi*, Yangon*
Independence: 4 January 1948 (from UK)
National holiday: Independence Day, 4 January (1948)
Constitution: 3 January 1974 (suspended since 18 September 1988); national convention started on 9 January 1993 to draft a new constitution; chapter headings and three of 15 sections have been approved
Legal system: does not accept compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: Prime Minister and Chairman of the State Peace and
Development Council Gen. THAN SHWE (since 23 April 1992); note—the prime
minister is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government: Prime Minister and Chairman of the State Peace
and Development Council Gen. THAN SHWE (since 23 April 1992); note—the
prime minister is both the chief of state and head of government
cabinet: State Peace and Development Council (SPDC); military junta,
so named 15 November 1997, which initially assumed power 18 September 1988
under the name State Law and Order Restoration Council; the SPDC oversees
the cabinet
elections: none; the prime minister assumed power upon resignation
of the former prime minister
Legislative branch: unicameral People's Assembly or Pyithu Hluttaw (485
seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections: last held 27 May 1990, but Assembly never convened
election results: percent of vote by party—NA%; seats by party—NLD
396, NUP 10, other 79
Judicial branch: limited; remnants of the British-era legal system in place, but there is no guarantee of a fair public trial; the judiciary is not independent of the executive
Political parties and leaders: Union Solidarity and Development Association (USDA, proregime), THAN AUNG, general secretary; National Unity Party (NUP, proregime), THA KYAW; National League for Democracy (NLD), AUNG SHWE, chairman, AUNG SAN SUU KYI, general secretary; and eight minor legal parties
Political pressure groups and leaders: National Coalition Government of the Union of Burma (NCGUB), headed by Dr. SEIN WIN—consists of individuals legitimately elected to the People's Assembly but not recognized by the military regime; the group fled to a border area and joined with insurgents in December 1990 to form a parallel government; Kachin Independence Army (KIA); United Wa State Army (UWSA); Karen National Union (KNU); several Shan factions; All Burma Student Democratic Front (ABSDF)
International organization participation: AsDB, ASEAN, CCC, CP, ESCAP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Intelsat (nonsignatory user), Interpol, IOC, ITU, NAM, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WMO, WToO, WTrO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador TIN WINN
chancery: 2300 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 332-9044, 9045
FAX: [1] (202) 332-9046
consulate(s) general: New York
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Kent M. WIEDEMANN
embassy: 581 Merchant Street, Rangoon (GPO 521)
mailing address: Box B, APO AP 96546
telephone: [95] (1) 282055, 282181 (operator assistance required)
FAX: [95] (1) 280409
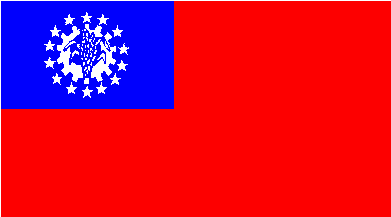
Flag description: red with a blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing, all in white, 14 five-pointed stars encircling a cogwheel containing a stalk of rice; the 14 stars represent the 14 administrative divisions
Economy—overview: Burma has a mixed economy with private activity dominant in agriculture, light industry, and transport, and with substantial state-controlled activity, mainly in energy, heavy industry, and the rice trade. Government policy in the last nine years, 1989-97, has aimed at revitalizing the economy after three decades of tight central planning. Thus, private activity has markedly increased; foreign investment has been encouraged, so far with moderate success; and efforts continue to increase the efficiency of state enterprises. Published estimates of Burma's foreign trade are greatly understated because of the volume of black-market trade. A major ongoing problem is the failure to achieve monetary and fiscal stability. Although Burma remains a poor Asian country, its rich resources furnish the potential for substantial long-term increases in income, exports, and living standards.
GDP: purchasing power parity—$55.7 billion (1997 est.)
GDP—real growth rate: 6% (1997 est.)
GDP—per capita: purchasing power parity—$1,190 (1997 est.)
GDP—composition by sector:
agriculture: 61%
industry: 10%
services: 29% (1996 est.)
Inflation rate—consumer price index: 30%-40% (1997 est.)
Labor force:
total: 18.8 million (FY95/96 est.)
by occupation: agriculture 65.2%, industry 14.3%, trade 10.1%, government
6.3%, other 4.1% (FY88/89 est.)
Unemployment rate: NA%
Budget:
revenues: $7.9 billion
expenditures: $12.2 billion, including capital expenditures of $5.7
billion (FY96/97)
Industries: agricultural processing; textiles and footwear; wood and wood products; copper, tin, tungsten, iron; construction materials; pharmaceuticals; fertilizer
Industrial production growth rate: 9.2% (FY95/96 est.)
Electricity—capacity: 1.212 million kW (1995)
Electricity—production: 4.1 billion kWh (FY95/96 est.)
Electricity—consumption per capita: 79 kWh (1995)
Agriculture—products: paddy rice, corn, oilseed, sugarcane, pulses; hardwood
Exports:
total value: $693 million (1996)
commodities: pulses and beans, teak, rice, rubber, hardwood
partners: Singapore, China, Indonesia, India, Thailand
Imports:
total value: $1.4 billion (1996)
commodities: machinery, transport equipment, construction materials,
food products, consumer goods
partners: Japan, Singapore, China, Thailand, Malaysia
Debt—external: $5.3 billion (FY94/95 est.)
Economic aid:
recipient: ODA, $61 million (1993)
Currency: 1 kyat (K) = 100 pyas
Exchange rates: kyats (K) per US$1—6.3941 (January 1998) 6.2418 (1997), 5.9176 (1996), 5.6670 (1995), 5.9749 (1994), 6.1570 (1993); unofficial—310-350 (1998)
Fiscal year: 1 April—31 March
Telephones: 122,195 (1993 est.)
Telephone system: meets minimum requirements for local and intercity
service for business and government; international service is good
domestic: NA
international: satellite earth station—1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean)
Radio broadcast stations: AM 2, FM 1, shortwave 0 (1985 est.)
note: radiobroadcast coverage is limited to the most populous areas
Radios: NA
Television broadcast stations: 1 (1988 est.)
Televisions: 88,000 (1992 est.)
Railways:
total: 3,569 km
narrow gauge: 3,569 km 1.000-m gauge (1995)
Highways:
total: 28,200 km
paved: 3,440 km
unpaved: 24,760 km (1996 est.)
Waterways: 12,800 km; 3,200 km navigable by large commercial vessels
Pipelines: crude oil 1,343 km; natural gas 330 km
Ports and harbors: Bassein, Bhamo, Chauk, Mandalay, Moulmein, Myitkyina, Rangoon, Akyab (Sittwe), Tavoy
Merchant marine:
total: 45 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 561,786 GRT/742,450 DWT
ships by type: bulk 15, cargo 18, chemical tanker 1, container 2, oil
tanker 3, passenger-cargo 3, refrigerated cargo 1, vehicle carrier 2
note: a flag of convenience registry; includes ships of 2 countries:
Japan owns 2 ships, US 3 (1997 est.)
Airports: 80 (1997 est.)
Airports—with paved runways:
total: 24
over 3,047 m: 3
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 12
914 to 1,523 m: 7 (1997 est.)
Airports—with unpaved runways:
total: 56
over 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 19
under 914 m: 32 (1997 est.)
Heliports: 1 (1997 est.)
Military branches: Army, Navy, Air Force
Military manpower—military age: 18 years of age
Military manpower—availability:
males age 15-49: 12,208,916
females age 15-49: 11,983,225 (1998 est.)
note: both sexes liable for military service
Military manpower—fit for military service:
males: 6,523,797
females: 6,387,291 (1998 est.)
Military manpower—reaching military age annually:
males: 488,818
females: 469,850 (1998 est.)
Military expenditures—dollar figure: $380 million (FY96/97 est.)
Military expenditures—percent of GDP: NA%
Disputes—international: none
Illicit drugs: world's largest illicit producer of opium (cultivation in 1997—155,150 hectares, a 5% decline from 1996; potential production—2,365 metric tons, an 8% drop from 1996) and a minor producer of cannabis for the international drug trade; surrender of drug warlord KHUN SA's Mong Tai Army in January 1996 was hailed by Rangoon as a major counternarcotics success, but lack of serious government commitment and resources continue to hinder the overall antidrug effort; growing role in the production of methamphetamines for regional consumption
This page last updated on 24 June 1998
Designed by Britt A. Cartrite,
1999