


 |
(MIDI player required) |
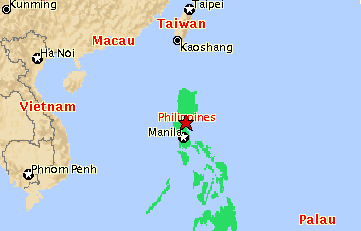
Republic of the Philippines
Location: Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Philippine Sea and the South China Sea, east of Vietnam
Geographic coordinates: 13 00 N, 122 00 E
Map references: Southeast Asia
Area:
total: 300,000 sq km
land: 298,170 sq km
water: 1,830 sq km
Area—comparative: slightly larger than Arizona
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 36,289 km
Maritime claims: measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
continental shelf: to depth of exploitation
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
territorial sea: irregular polygon extending up to 100 nm from coastline as defined by
1898 treaty; since late 1970s has also claimed polygonal-shaped area in South
China Sea up to 285 nm in breadth
Climate: tropical marine; northeast monsoon (November to April); southwest monsoon (May to October)
Terrain: mostly mountains with narrow to extensive coastal lowlands
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Philippine Sea 0 m
highest point: Mount Apo 2,954 m
Natural resources: timber, petroleum, nickel, cobalt, silver, gold, salt, copper
Land use:
arable land: 19%
permanent crops: 12%
permanent pastures: 4%
forests and woodland: 46%
other: 19% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 15,800 sq km (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: astride typhoon belt, usually affected by 15 and struck by five to six cyclonic storms per year; landslides; active volcanoes; destructive earthquakes; tsunamis
Environment—current issues: uncontrolled deforestation in watershed areas; soil erosion; air and water pollution in Manila; increasing pollution of coastal mangrove swamps which are important fish breeding grounds
Environment—international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes,
Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection,
Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification
Population: 77,725,862 (July 1998 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 38% (male 14,867,972; female 14,379,722)
15-64 years: 59% (male 22,582,178; female 23,136,055)
65 years and over: 3% (male 1,232,813; female 1,527,122) (July 1998 est.)
Population growth rate: 2.09% (1998 est.)
Birth rate: 28.43 births/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Death rate: 6.52 deaths/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Net migration rate: -1.04 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1998 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female (1998 est.)
Infant mortality rate: 34.56 deaths/1,000 live births (1998 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 66.35 years
male: 63.57 years
female: 69.28 years (1998 est.)
Total fertility rate: 3.54 children born/woman (1998 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Filipino(s)
adjective: Philippine
Ethnic groups: Christian Malay 91.5%, Muslim Malay 4%, Chinese 1.5%, other 3%
Religions: Roman Catholic 83%, Protestant 9%, Muslim 5%, Buddhist and other 3%
Languages: Pilipino (official, based on Tagalog), English (official)
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 94.6%
male: 95%
female: 94.3% (1995 est.)
Country name:
conventional long form: Republic of the Philippines
conventional short form: Philippines
local long form: Republika ng Pilipinas
local short form: Pilipinas
Data code: RP
Government type: republic
National capital: Manila
Administrative divisions: 72 provinces and 61 chartered cities*; Abra, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Aklan, Albay, Angeles*, Antique, Aurora, Bacolod*, Bago*, Baguio*, Bais*, Basilan, Basilan City*, Bataan, Batanes, Batangas, Batangas City*, Benguet, Bohol, Bukidnon, Bulacan, Butuan*, Cabanatuan*, Cadiz*, Cagayan, Cagayan de Oro*, Calbayog*, Caloocan*, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Camiguin, Canlaon*, Capiz, Catanduanes, Cavite, Cavite City*, Cebu, Cebu City*, Cotabato*, Dagupan*, Danao*, Dapitan*, Davao City* Davao, Davao del Sur, Davao Oriental, Dipolog*, Dumaguete*, Eastern Samar, General Santos*, Gingoog*, Ifugao, Iligan*, Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, Iloilo, Iloilo City*, Iriga*, Isabela, Kalinga-Apayao, La Carlota*, Laguna, Lanao del Norte, Lanao del Sur, Laoag*, Lapu-Lapu*, La Union, Legaspi*, Leyte, Lipa*, Lucena*, Maguindanao, Mandaue*, Manila*, Marawi*, Marinduque, Masbate, Mindoro Occidental, Mindoro Oriental, Misamis Occidental, Misamis Oriental, Mountain, Naga*, Negros Occidental, Negros Oriental, North Cotabato, Northern Samar, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Olongapo*, Ormoc*, Oroquieta*, Ozamis*, Pagadian*, Palawan, Palayan*, Pampanga, Pangasinan, Pasay*, Puerto Princesa*, Quezon, Quezon City*, Quirino, Rizal, Romblon, Roxas*, Samar, San Carlos* (in Negros Occidental), San Carlos* (in Pangasinan), San Jose*, San Pablo*, Silay*, Siquijor, Sorsogon, South Cotabato, Southern Leyte, Sultan Kudarat, Sulu, Surigao*, Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur, Tacloban*, Tagaytay*, Tagbilaran*, Tangub*, Tarlac, Tawitawi, Toledo*, Trece Martires*, Zambales, Zamboanga*, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur
Independence: 4 July 1946 (from US)
National holiday: Independence Day, 12 June (1898) (from Spain)
Constitution: 2 February 1987, effective 11 February 1987
Legal system: based on Spanish and Anglo-American law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: President Fidel Valdes RAMOS (since 30 June 1992) and Vice President
Joseph Ejercito ESTRADA (since 30 June 1992); note—the president is both
the chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Fidel Valdes RAMOS (since 30 June 1992) and Vice President
Joseph Ejercito ESTRADA (since 30 June 1992); note—the president is both
the chief of state and head of government
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president with the consent of the Commission
of Appointments
elections: president and vice president elected on separate tickets by popular
vote for six-year terms; election last held 11 May 1992 (next to be held 11
May 1998)
election results: Fidel Valdes RAMOS elected president; percent of vote—Fidel Valdes
RAMOS 23.6% (a narrow plurality); Joseph Ejercito ESTRADA elected vice president;
percent of vote—NA%
Legislative branch: bicameral Congress or Kongreso consists of the Senate or Senado (24
seats—one-half elected every three years; members elected by popular vote
to serve six-year terms) and the House of Representatives or Kapulungan Ng
Mga Kinatawan (204 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve three-year
terms; note—an additional 50 members may be appointed by the president)
elections: Senate—last held 8 May 1995 (next to be held 11 May 1998); House of
Representatives—elections last held 8 May 1995 (next to be held 11 May 1998)
election results: Senate—percent of vote by party—NA; seats by party—LDP 15, Lakas-NUCD
6, NPC 1, PRP 1, independent 1; House of Representatives—percent of vote
by party—NA; seats by party—Lakas-NUCD 126, LDP 28, NPC 28, NP 2, KBL
2, other 18
Judicial branch: Supreme Court, justices are appointed for four-year terms by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial and Bar Council
Political parties and leaders: Democratic Filipino Struggle (Laban ng Demokratikong Pilipino, LDP),
Edgardo ANGARA; People Power-National Union of Christian Democrats (Lakas
ng EDSA-NUCD or Lakas-NUCD), Jose DE VENECIA, secretary general; Liberal Party
(LP), Alfredo LIM, standard bearer; Laban Ng Makabayang Masang Pilipino (LMMP
or Fight of the Patriotic Filipino Masses), Joseph ESTRADA, standard bearer;
National People's Coalition (NPC), Eduardo COJUANGCO; People's Reform Party
(PRP), Miriam DEFENSOR-SANTIAGO; New Society Movement (Kilusan Bagong Lipunan,
KBL), Imelda MARCOS; Nacionalista Party (NP), Salvador H. LAUREL, president;
Filipino Democratic Party (Partido Demokratikong Philipinas or PDP), Jose
COJUANGCO, is part of the ruling coalition with the LDP
note: political parties are highly fluid and personalistic; the major parties
as of May 1998 are—Lakas-NUCD, LMMP, and LP
International organization participation: APEC, AsDB, ASEAN, CCC, CP, ESCAP, FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Inmarsat, Intelsat, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO, ITU, NAM, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNU, UPU, WCL, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTrO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Raul Chaves RABE
chancery: 1600 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: [1] (202) 467-9300
FAX: [1] (202) 328-7614
consulate(s) general: Agana (Guam), Chicago, Honolulu, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco,
and Seattle
consulate(s): San Jose (Saipan)
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Thomas C. HUBBARD
embassy: 1201 Roxas Boulevard, Ermita Manila 1000
mailing address: FPO 96515
telephone: [63] (2) 523-1001
FAX: [63] (2) 522-4361
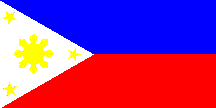
Flag description: two equal horizontal bands of blue (top) and red with a white equilateral triangle based on the hoist side; in the center of the triangle is a yellow sun with eight primary rays (each containing three individual rays) and in each corner of the triangle is a small yellow five-pointed star
Economy—overview: In 1997 the Philippine economy, primarily a mixture of agriculture and light industry, continued its fifth year of positive economic growth, led by expansion of exports and investment. The government expects growth to slow to about 3% in 1998 due to spillover effects of the financial crisis in East Asia. The government has promised to continue its economic reforms to help the Philippines match the pace of development in the newly industrialized countries of East Asia. The strategy includes improving infrastructure, overhauling the tax system to bolster government revenues, and moving toward further deregulation and privatization of the economy.
GDP: purchasing power parity—$244 billion (1997 est.)
GDP—real growth rate: 5.1% (1997 est.)
GDP—per capita: purchasing power parity—$3,200 (1997 est.)
GDP—composition by sector:
agriculture: 22%
industry: 32%
services: 46% (1996 est.)
Inflation rate—consumer price index: 5.1% (1997)
Labor force:
total: 29.13 million (1996 est.)
by occupation: agriculture 43.4%, services 22.6%, government services 17.9%, industry
and commerce 16.1% (1995)
Unemployment rate: 8.7% (1997)
Budget:
revenues: $16.3 billion
expenditures: $16.6 billion, including capital expenditures of $2.7 billion (1996
est.)
Industries: textiles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, wood products, food processing, electronics assembly, petroleum refining, fishing
Industrial production growth rate: 6.3% (1996)
Electricity—capacity: 7.64 million kW (1995)
Electricity—production: 25.65 billion kWh (1995)
Electricity—consumption per capita: 350 kWh (1995)
Agriculture—products: rice, coconuts, corn, sugarcane, bananas, pineapples, mangoes; pork, eggs, beef; fish catch of 2 million metric tons annually
Exports:
total value: $25 billion (f.o.b., 1997 est.)
commodities: electronics and telecommunications 51%, machinery and transport 10%,
garments 9%, other 30%
partners: US 34%, Japan 17%, EU 17%, ASEAN 14%, Hong Kong 4%, Taiwan 4% (1997
est.)
Imports:
total value: $34 billion (f.o.b., 1997 est.)
commodities: raw materials and intermediate goods 43%, capital goods 36%, consumer
goods 9%, fuels 9%
partners: Japan 21%, US 20%, ASEAN 12%, EU 10%, Taiwan 5%, Hong Kong 4%, Saudi
Arabia 4% (1997 est.)
Debt—external: $45.4 billion (December 1997)
Economic aid:
recipient: ODA, $3 billion pledged at December 1997 for 1998
Currency: 1 Philippine peso (P) = 100 centavos
Exchange rates: Philippine pesos (P) per US$1—40.2 (April 1998), 26.36 (May 1997), 29.471 (1997), 26.216 (1996), 25.714 (1995), 26.417 (1994), 27.120 (1993)
Fiscal year: calendar year
Telephones: 1.9 million (1997)
Telephone system: good international radiotelephone and submarine cable services; domestic
and interisland service adequate
domestic: domestic satellite system with 11 earth stations
international: submarine cables to Hong Kong, Guam, Singapore, Taiwan, and Japan; satellite
earth stations—3 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean and 2 Pacific Ocean)
Radio broadcast stations: AM 261, FM 55, shortwave 0
Radios: 9.03 million (1992 est.)
Television broadcast stations: 29
Televisions: 9.2 million (1998)
Railways:
total: 897 km of which 492 km in operation
narrow gauge: 492 km 1.067-m gauge (1996)
Highways:
total: 156,997 km (1996 est.)
paved: NA km
unpaved: NA km
note: probably less than 30,000 km are designated arterial roads and not all
of these are all-weather roads
Waterways: 3,219 km; limited to shallow-draft (less than 1.5 m) vessels
Pipelines: petroleum products 357 km
Ports and harbors: Batangas, Cagayan de Oro, Cebu, Davao, Guimaras Island, Iligan, Iloilo, Jolo, Legaspi, Manila, Masao, Puerto Princesa, San Fernando, Subic Bay, Zamboanga
Merchant marine:
total: 535 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 7,334,164 GRT/11,511,707 DWT
ships by type: bulk 206, cargo 130, chemical tanker 5, combination bulk 12, container
11, liquefied gas tanker 10, livestock carrier 12, oil tanker 48, passenger
4, passenger-cargo 13, refrigerated cargo 20, roll-on/roll-off cargo 15, short-sea
passenger 31, vehicle carrier 18
note: a flag of convenience registry; Japan owns 21 ships, Hong Kong 4, Cyprus
1, Denmark 1, Greece 1, Netherlands 1, Norway 1, Panama 1, Singapore 1, and
Taiwan 1 (1997 est.)
Airports: 262 (1997 est.)
Airports—with paved runways:
total: 75
over 3,047 m: 3
2,438 to 3,047 m: 7
1,524 to 2,437 m: 25
914 to 1,523 m: 30
under 914 m: 10 (1997 est.)
Airports—with unpaved runways:
total: 187
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 63
under 914 m: 121 (1997 est.)
Heliports: 1 (1997 est.)
Military branches: Army, Navy (includes Coast Guard and Marine Corps), Air Force
Military manpower—military age: 20 years of age
Military manpower—availability:
males age 15-49: 19,734,347 (1998 est.)
Military manpower—fit for military service:
males: 13,921,259 (1998 est.)
Military manpower—reaching military age annually:
males: 800,148 (1998 est.)
Military expenditures—dollar figure: $1.3 billion (1996)
Military expenditures—percent of GDP: 0.7% (1996)
Disputes—international: involved in a complex dispute over the Spratly Islands with China, Malaysia, Taiwan, Vietnam, and possibly Brunei; claims Malaysian state of Sabah
Illicit drugs: exports locally-produced marijuana and hashish to East Asia, the US, and other Western markets; serves as a transit point for heroin and crystal methamphetamine
This page last updated on 29 June 1999
Designed by Britt A. Cartrite,
1999