Econ 2012 Section 5 Principles of Macroeconomics, Midterm 1 (September 28, 1998), Fall 1998
Instructor: Vijaya Sharma, University of Colorado at Denver
Instructions:
The test has 40 multiple choice questions. Each question carries equal weight. Use the separately provided answer sheet to circle the correct choice in each question. Hand in the answer sheet only when you are done.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. The opportunity cost of a good or service is the
a. actual dollar cost of providing it.
b. highest price that a seller can get.
c. value of the next best alternative.
d. cost associated with a value judgment.
2. You have just bought a used car, and drive away satisfied that you've made a good deal on the purchase. What would an economist say about your "gain" on the deal?
a. Your gain has clearly meant that the seller lost on the deal.
b. The seller has clearly gained, and you have actually lost on the deal.
c. Both you and the seller have gained something.
d. If your gain is too large, then the deal should be re-negotiated.
3. The fact that resources tend to be specialized is one reason the production possibilities frontier is drawn
a. bowed outward.
b. bowed inward.
c. as a straight line (but not horizontal).
d. as a horizontal straight line.
4. The supply curve shows
a. the relationship between amount of production and technology.
b. who will have an opportunity to produce or purchase an item.
c. the quantity supplied as a function of the price.
d. plots of what quantities have been sold over the past few weeks or months.
5. Is faster economic growth unambiguously better?
a. No, because growth has an opportunity cost.
b. Yes, because more goods and services are always better.
c. Yes, because it expands the production possibilities of an economy.
d. Uncertain--economic growth has no answer to this question.
6. An increase in the price of gasoline shifts the demand for tires to the
a. left, because gasoline and tires are substitutes.
b. left, because gasoline and tires are normally used together.
c. right, because gasoline and tires are substitutes.
d. right, because gasoline and tires are normally used together.
7. Suppose that in a free market 2,000 patients purchase an operation to receive an artificial heart at a price of $500,000 per operation. Without the heart, each patient will die. The government decides this price is too high and imposes a maximum price of $200,000. Everything else equal,
a. more patients will now die.
b. fewer patients will now die.
c. more patients will now die only if the demand curve is vertical.
d. more patients will now die only if the demand curve is horizontal.
8. In an attempt to reduce poaching of elephant tusks for ivory, officials in Kenya burned illegally gathered ivory. Economists tend to point out that
a. the supply of ivory has fallen, leading to an increase in price and reward
for poaching.
b. burning ivory decreases demand, leading to lower prices and reward for
poaching.
c. the demand for ivory is higher, leading to an increase in price and reward
for poaching.
d. burning ivory raises demand, and controlled prices will lead to even
greater poaching.
9. When a teacher in a private school tells her principal that since all classrooms have empty seats the cost of additional students is really zero, she is using the
a. law of comparative advantage.
b. principle of marginal analysis.
c. theory of externalities.
d. concept of opportunity cost.
10. The difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics is that
11. A movement along the supply curve as the price of a product changes is called a
a. change in quantity supplied.
b. change in supply.
c. supply shift.
d. substitution effect.
12. Voters often choose to remain ignorant because
13. A local florist grows flowers in a plot of land. Her flowers are exceptionally colorful and admired by neighbors. There is no way the florist can charge neighbors for enjoyment her flowers offer to them. We can safely conclude that
14. Lines, ration coupons, and black markets are symptoms of a
a. price floor.
b. price ceiling.
c. free market.
d. barter economy.
15. What decision rule should be followed to maximize the net benefit of some activity?
a. Choose the level of activity at which marginal cost = zero.
b. Choose the level at which marginal benefit = zero.
c. Choose the level at which marginal benefit = marginal cost.
d. Choose the level at which total benefit = total cost.
Table 3-1
Peanuts Corn
(Bushels) (Bushels)
0 55
10 50
20 42
30 28
40 0
16. Suppose a farmer produces 10 bushels of peanuts and 50 bushels of corn. According to Table 3-1, the opportunity cost of peanuts is
a. 8/10 bushels of corn.
b. 42 bushels of corn.
c. 50 bushels of corn.
d. impossible to determine from the information given.
17. If economic efficiency is the criterion, which of the following is the most important justification for the government to provide certain economic goods or services?
18. Two studies published in the New England Journal of Medicine link the risk of breast cancer to alcohol consumption. Young women who have nine drinks per week were reportedly 150 percent more likely to develop breast cancer. Considering the market for alcohol, an economist would predict a movement
a. up the demand curve as quantity demanded falls.
b. up the supply curve as the demand curve shifts.
c. down the supply curve as the demand curve shifts.
d. down the demand curve as quantity demanded falls.
19. To be effective, a price floor must be
a. above the equilibrium price.
b. at the equilibrium price.
c. below the equilibrium price.
d. anywhere on the graph.
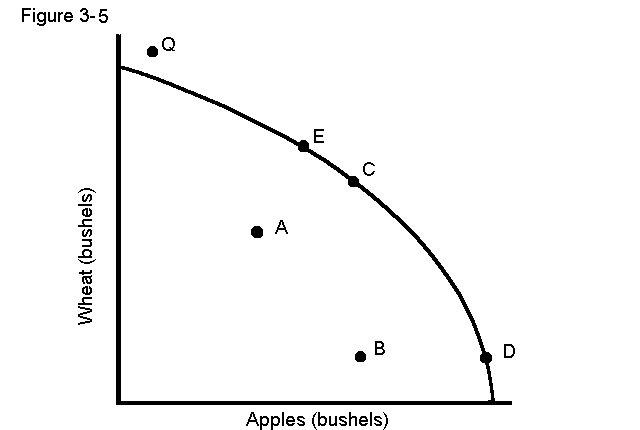
20. In Figure 3-5, for which of the following would this statement be true: "To get more apples we have to give up wheat." A movement from
a. A to E
b. C to D
c. D to E
d. B to C

21. If the price of a good is below the equilibrium price,
a. suppliers will find inventories building; they will cut output and raise
prices.
b. suppliers will find inventories being depleted and will increase production
and raise prices.
c. the demand curve will shift down until an equilibrium is established at the
existing price.
d. the supply curve will shift up until an equilibrium is established at the
existing price.
22. Goods and services from which it is difficult to exclude nonpaying customers are called
23. If trade between two countries is voluntary, one can expect that
a. one country's gain is necessarily the other's loss.
b. neither country really gains from the trade.
c. the larger country will always gain at the expense of the smaller.
d. both countries expect to gain something.
24. Which person has the highest opportunity cost of obtaining a college degree (assuming that attending college requires giving up their current position)?
a. Bill, who is unemployed.
b. Jane, who is an unwed mother and earns $15,000 a year.
c. Mary, who has a job earning $60,000 a year as a computer programmer.
e. Unable to determine from the data given.
25. If a decision-maker uses marginal analysis, then the relevant costs are
a. the full cost of a particular activity or product.
b. the costs which are invariant to the extra activity or product.
c. the profit obtained on the activity or product.
d. the extra costs for a particular activity or product.
26. Because there is a trade-off between output and equality of distribution
a. greater equality of distribution will generally result in higher levels of
output.
b. greater output is generally associated with more equal distribution.
c. policies designed to increase output will only succeed if distribution is
more equal.
d. policies designed to equalize distribution may adversely affect the size of
output.
27. If Taiwanese workers can produce everything more cheaply than American workers:
a. Americans can still gain by trading with Taiwan.
b. Americans can only lose if they import from Taiwan.
c. Taiwan can only lose if it trades with America.
d. There are no gains from trade that are possible in this case.
28. Rent control is usually justified on the ground that it protects moderate to low income families from the burden of rapidly rising rents and from eviction if they are not able to pay. It also prevents landlords from reaping windfalls as property values rise. Opponents note that rent controls usually lead to a reduced supply of rental housing and shortages. The proponents of rent controls support them primarily on the grounds of
a. efficiency.
b. equality.
c. externalities.
d. free riding.
29. The central question in economics is how to
a. make the best use of scarce resources.
b. use government planning agencies.
c. induce people to want less.
d. increase human knowledge.
30. A production possibilities curve always slopes downward to the right because
a. resources are not scarce.
b. resources have no opportunity cost.
c. resources are freely available.
d. resources are limited.
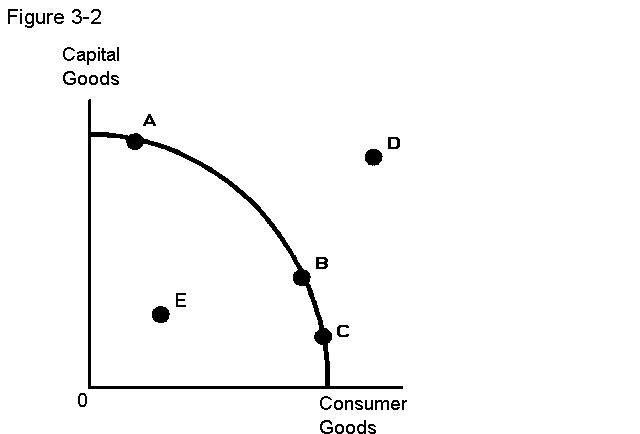
31. In Figure 3-2, a point such as E
a. is not obtainable.
b. is an efficient use of resources.
c. represents a misallocation of resources.
d. indicates that the society is a capitalist society.
32. The slope of a demand curve is almost always
a. positive, because when people buy more of a good the cost of producing it
will rise.
b. positive, because the more money a person has, the more of a particular
good will be bought.
c. negative, because when people buy more of a good the cost of producing it
will fall.
d. negative, because with everything else equal, the same people will buy more
of a good when its price is lower.
33. According to the short-sightedness effect,
34. Firms often seek to borrow money to expand their capital stock, and the price they pay for the money is the interest rate. What happens to demand for money if the interest rate increases?
a. It increases.
b. It decreases.
c. It does not change.
d. Uncertain--economic theory has no answer to this question.
35. Which of the following is the correct way to describe equilibrium in a market?
a. At equilibrium, demand equals supply.
b. At equilibrium quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
c. At equilibrium, market forces are no longer at work.
d. Equilibrium is the best combination of price and quantity.
36. When production of a good generates external costs, market allocation, compared to the efficient allocation, will likely result in an output level that is too
37. The supply curve is upward-sloping because of
a. improving efficiency as output expands.
b. the principle of increasing costs.
c. collusion among suppliers to raise prices.
d. the "charge what the market will bear" attitude of sellers.
38. Which of the following statements is correct?
39. A person who consumes a good without paying for it is called a(n)
40. The primary reason governments intervene in a market characterized by imperfect competition is
***********************************************************************
Answer Key of Midterm 1
Econ 2012 Section 5 Principles of Macroeconomics
University of Colorado at Denver, Fall 1998
|
Question Number |
Correct Choice |
Question Number |
Correct Choice |
|
1 |
c |
21 |
b |
|
2 |
c |
22 |
d |
|
3 |
a |
23 |
d |
|
4 |
c |
24 |
c |
|
5 |
a |
25 |
d |
|
6 |
b |
26 |
d |
|
7 |
a |
27 |
a |
|
8 |
a |
28 |
b |
|
9 |
d |
29 |
a |
|
10 |
b |
30 |
d |
|
11 |
a |
31 |
c |
|
12 |
b |
32 |
d |
|
13 |
b |
33 |
c |
|
14 |
b |
34 |
c |
|
15 |
c |
35 |
b |
|
16 |
a |
36 |
b |
|
17 |
d |
37 |
b |
|
18 |
c |
38 |
c |
|
19 |
a |
39 |
d |
|
20 |
b |
40 |
a |